On this article, we will analyse a variant of a malware called Yobfy. This article is mainly focus on the technique used to unpack this sample and a shot chapter will presents a static analysis of the malware and how to find the CC used by this specific sample
Packer
Most part of the packer’s functions are encrypted.
We can identify this portion by seeking this patern.

We notice that, after the call, they are some garbage. The called functions applied a XOR on this part. When the function exits we have a correct code.

This is the decoding function.
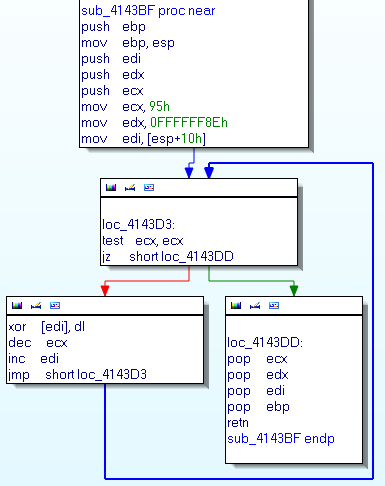
To recover all the used functions we wrote a script in python. This script decodes all functions so we can analyse it with IDA.
#!/bin/python
import sys
data = bytearray(open(sys.argv[1]).read())
infos = [
{ 'start': 0xEE00, 'key': 0x33, 'len': 0x1000 },
{ 'start': 0x15ED, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x95 },
{ 'start': 0x70f, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x56 },
{ 'start': 0x169D, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0xbf },
{ 'start': 0x822, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x79 },
{ 'start': 0x177d, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x1f },
{ 'start': 0x20f0, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x187 },
{ 'start': 0x22fb, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x54 },
{ 'start': 0x8BD, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x43 },
{ 'start': 0x0926, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x0abe, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x0c56, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x0dee, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x0f86, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x111e, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x12b6, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x144e, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x173 },
{ 'start': 0x17b5, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x3f },
{ 'start': 0x180d, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x3e },
{ 'start': 0x186b, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x38 },
{ 'start': 0x18c3, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x18 },
{ 'start': 0x1900, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x4b2 },
{ 'start': 0x1dc9, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0xab },
{ 'start': 0x1e95, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x30 },
{ 'start': 0x1eee, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x84 },
{ 'start': 0x1f8f, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x9a },
{ 'start': 0x203f, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x99 },
{ 'start': 0x2291, 'key': 0x8e, 'len': 0x54 },
]
for i in infos:
for j in range(i['start'], i['start'] + i['len']):
data[j] ^= i['key']
open(sys.argv[1] + "-patched", 'w').write(data)
Note the packer used the TLS callback to run the packer’s function. The entry point of the packer is 401260h and not the start function.
A idb of this patched binary is available here
Encrypted binary
The encrypted binary is in the section
qguttpj 00415000h - 0041B000h
The function at address 00402CE2h (decodeMZ) is used to decode this section
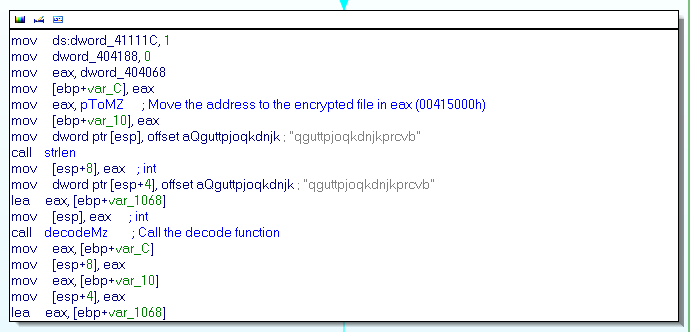
Process Injection
The function at address 004024F0h (injection) is used to run the decrypted binary, it used the classic set of function CreateProcess, NtUmapViewOfSection, WriteProcessMemory… All this founctions are load with GetProcAddress.

Unpack
To unpack it, the easier way is to put a breakpoint on WriteProcessMemory. At this breakpoint, the packer writes the unpacked binary in a new process.
Note: to avoid to be infected before you can put the breakpoint you have to change ollydbg settings to stop on TLS callback
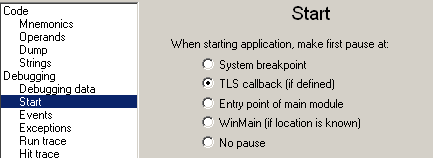
Put the breakpoint on Kernel32:WriteProcessMemory
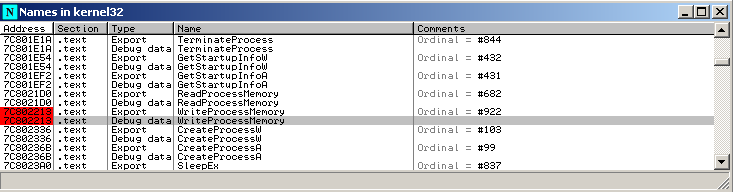
And continue
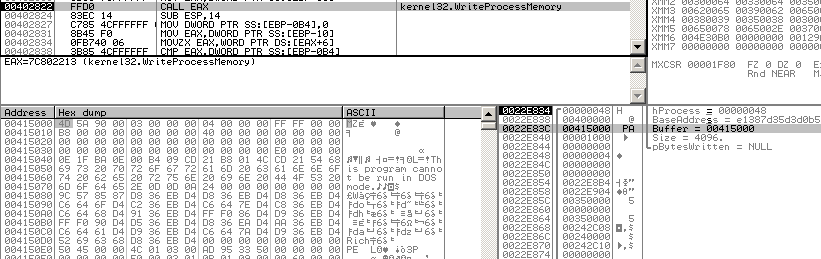
We get the MZ, dump the memory page.
The last files is a UPX packed binary.
y0ug@malware.lu:~/Share/VM/normal$ file unpack.bin
unpack.bin: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows, UPX compressed
y0ug@malware.lu:~/Share/VM/normal$ upx -d unpack.bin
y0ug@malware.lu:~/Share/VM/normal$ md5sum unpack.bin a56842a160da6ae661c2b7b3cc9a7e5c unpack.bin
Static Analysis
On IDA Pro we can identify encoded strings:
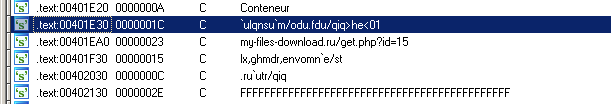
The function used to decode strings is sub_406A60.
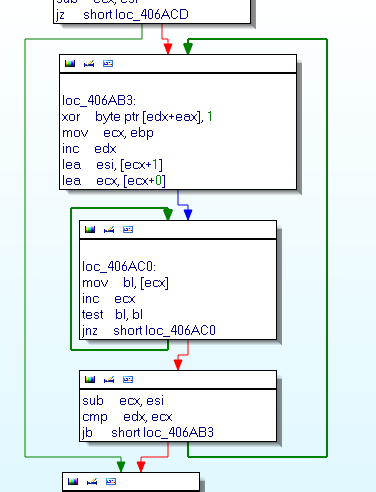
This function simply make a XOR 1, here a ruby script to decode strings:
#!/usr/bin/env ruby1.9.1
Astr=[]
malwareFile = File.open(ARGV[0], 'r')
malwareFile.seek(0x1230, IO::SEEK_SET)
Astr[0] = malwareFile.sysread(27)
malwareFile.seek(0x1330, IO::SEEK_SET)
Astr[1] = malwareFile.sysread(20)
key = 1
for str in Astr
str.each_byte { |x|
putc x^key
}
puts
end
rootbsd@malware.lu:~$ ./decode.rb e1387d35d3d0b59eb9eb68f08598cb6_00415000.bin
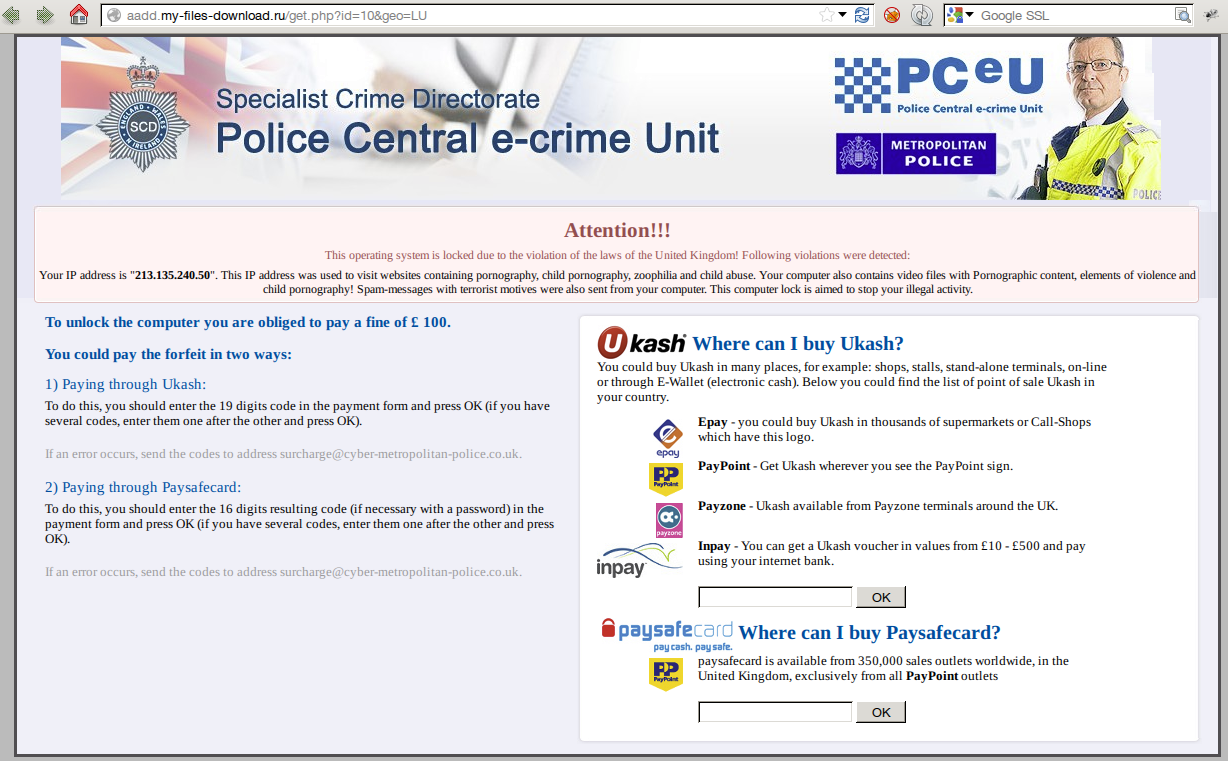
atmportal.net/get.php?id=10
my-files-download.ru
The C&C are identified. The apache configuration of the C&C allows to use a random subdomain. The domains wildcard are:
*.atmportal.net
*.my-files-download.ru
The malware generate a random subdomain.
Here an example of web page: